Mothers need to understand the difference between stunting and wasting in children, as it is crucial for ensuring proper nutritional adequacy from pregnancy through the early stages of the baby’s life.
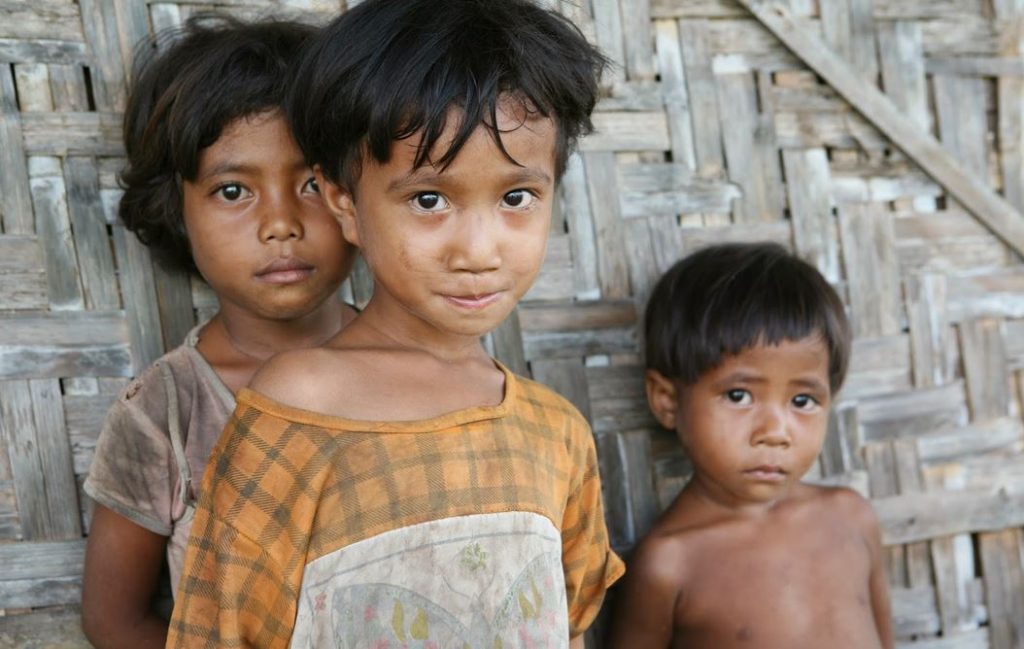

Many people still confuse stunting with wasting. Generally, stunting is identified by a child’s height being significantly below the average for their age. In contrast, wasting refers to malnutrition, where the child’s weight is disproportionately low compared to their height.
In Indonesia, the stunting prevalence stands at 21.6%, while Indonesia aims to reduce it to 14% by 2024. To help lower this high rate, it is crucial for mothers to understand the differences between stunting and wasting and address both issues effectively.
Difference Between Stunting and Wasting
As mentioned, although stunting and wasting are both nutritional issues frequently encountered by children, they have different underlying causes. Here are the key differences between stunting and wasting that are important to understand:
Stunting
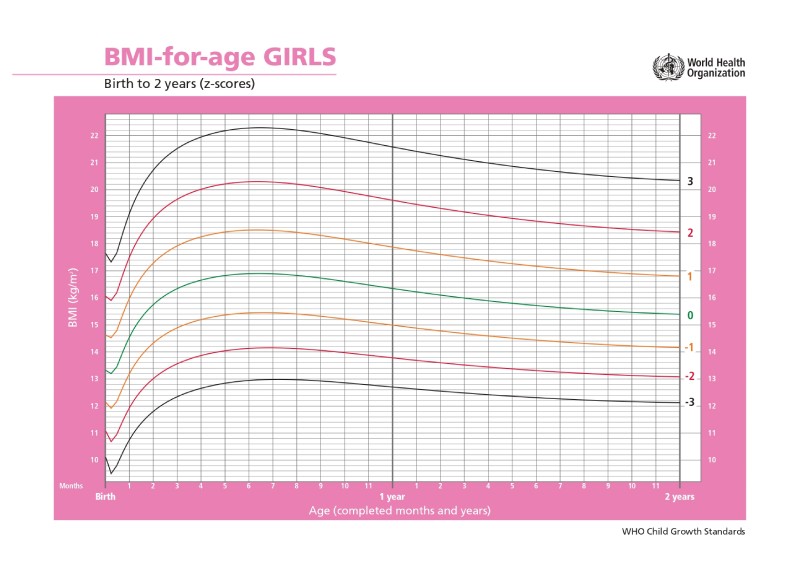
Stunting is a growth disorder primarily caused by chronic nutritional issues from pregnancy through the early stages of a child’s life, typically becoming apparent after the child turns 2 years old. According to the Indonesian Ministry of Health, a child is considered stunted if their length or height measurements fall below the normal range for their age. These measurements are assessed against the WHO child growth standards to determine if they fall within the normal range.
Currently, Indonesia uses the World Health Organization (WHO) growth curve as a reference tool for monitoring infant height.
To ensure your baby’s growth aligns with WHO guidelines, regularly visit the integrated health post or community health center. During each visit, have your child’s weight, length, and head circumference measured. However, having a shorter stature does not automatically mean a child is stunted. A pediatrician must distinguish stunting from other causes of short stature to determine the appropriate course of action. In some cases, short stature may require therapies such as leg lengthening, hormone replacement, or enzyme replacement.
Features of children with stunting:
- Delayed growth
- Poor performance on attention and memory tests
- Signs of delayed puberty
- Withdrawal and difficulty with eye contact between ages 8-10
- Appearing younger than their actual age
- Increased susceptibility to infectious diseases
Wasting
Wasting is a condition where a child’s weight decreases, is very low, or even below the normal range. Wasting can be said to be malnutrition which means the body does not get enough nutritional intake so it cannot meet the basic needs of growth, development, and body function.
Wasting is caused by malnutrition due to inadequate food intake and can also result from certain infections. Therefore, it is crucial for parents to ensure their children receive proper nutrition.
Among various nutritional issues in children, wasting poses the highest risk of mortality. Severe malnutrition, in particular, has a death risk nearly 12 times greater than that of well-nourished children.
Children diagnosed with wasting who do not receive appropriate care face a high risk of death. Those with untreated wasting are three times more likely to become stunted, and stunted children have a 1.5 times higher risk of developing wasting compared to well-nourished children.
According to WHO, a child is considered to have wasting when there is a significant decrease in weight while height continues to increase (weight-for-height ratio). A child is classified as wasted if their weight-for-height ratio falls between -3 and below -2 standard deviations (SD). Additionally, if the weight loss is more severe than usual, the child may be classified as acutely wasted.
Factors that cause children to be wasting
- Lack of access to health services, perhaps the problem of mothers being reluctant to take them to have their children checked for health conditions
- Provision of unfulfilled nutritional intake for children, such as Exclusive Breastfeeding, MP-ASI, and solid foods but with inadequate quantity and quality
- Unsanitary surrounding environment, the cause of difficulty in obtaining clean water and sanitation services.
- Lack of knowledge about nutrition and children’s health
- Limited and non-diverse food sources.
Stunting and wasting in toddlers in Indonesia are serious issues that should not be taken lightly. Recognizing the causes of malnutrition in children is a crucial first step in both prevention and management.
BB/TB (Body Weight and Height) is the best anthropometric measurement indicator because it can describe nutritional status sensitively and specifically. Body weight is linearly correlated with height, meaning that weight development will be followed by height.
Get Anthropometric Measuring Tools Products From PT. Solo Abadi Indonesia
PT Solo Abadi Indonesia is the largest manufacturing company and manufacturer of medical devices in Indonesia. Our company has been producing medical devices since 2020 and has been certified. PT Solo Abadi Indonesia has collaborated with more than 200 Health Offices. Kamai also provides anthropometry kit packages to help monitor children’s developmental conditions.

Our Anthropometry-kit package consists of a digital baby scale, a digital adult scale, an infatometer board, a stadiometer, a Lila measuring tool, and also an anthropometry bag. With the completeness of the bag and minimalist tools, you can carry the set of tools anywhere.
For your agency needs, you can buy it through E-Catalog. You can also order your needs through the ask for price form and get the best price. For direct purchases, you can contact our WhatsAapp.