Understanding the different types of bearings and their applications is crucial for recognizing components in the machinery world.
With the advancement of manufacturing technology worldwide, many supporting components have also evolved, one of which is the bearing. Bearings are components that play a role in mechanics and machinery.
What Is a Bearing?
A bearing is a mechanical component designed to minimize friction between parts of a machine, allowing them to move smoothly in their intended direction.
An example is the bearing used in car wheels to ensure the wheels rotate smoothly and reduce friction between the wheel axle and other parts. This helps to reduce wear and tear on the car’s wheels.

Bearing Functions
The main function of a bearing is to reduce friction between two objects that move relative to each other, such as between a shaft and its rotating axis. Bearings can also be used to support rotating objects.
Read More: Getting to Know the Types of Chisels Used in Lathes Machine
Types of Loads on Bearing
- Radial Load
Radial Load is a force applied perpendicular to the shaft axis of the bearing.
- Axial Load
Axial Load is a force that comes from the side of the bearing.
Parts of a Bearing and Their Functions
Below are the functions of the parts of a bearing:
- Outer Ring
The ring located on the outermost part functions to keep the balls in place while they rotate.
- Inner Ring
The inner ring is the part that directly contacts the shaft. Like the outer ring, the inner ring has a raceway that serves as the track for the rolling elements.
- Cage / Retainer
This component plays a role in adjusting the distance between the spherical and cylindrical components. Therefore, the balls or rollers cannot come into contact with or rub against other parts of the bearing.
- Seal
This part functions to protect or seal the interior of the bearing to keep it clean.
Types of Bearing
All types of bearings have their own functions and applications. A designer must understand the use and application of each type of bearing. Below are the types of bearings and their applications.
1. Ball Bearings
Ball bearing is one of the most commonly found types of bearings because it can handle both radial loads and thrust loads. However, it has a limitation: it is restricted to relatively small loads.
Considerations for Choosing a Bearing:
- Ball bearings are ideal for applications with high speeds. They are suitable for lower loads.
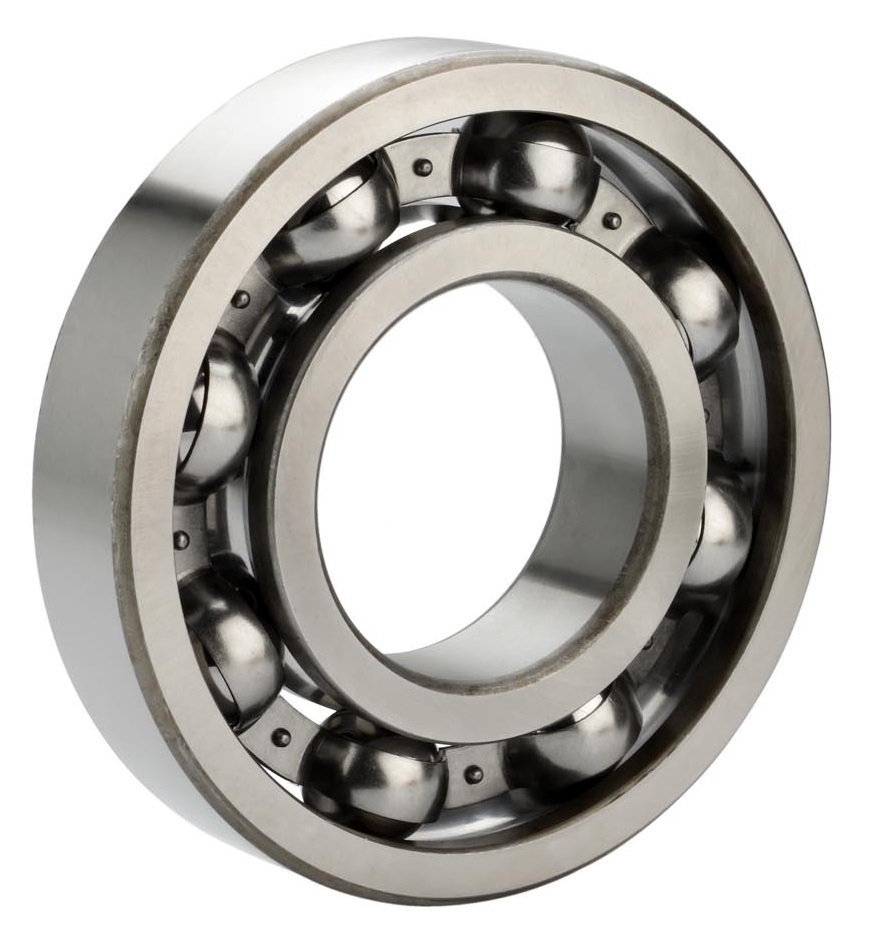

2. Roller Bearing
Roller bearings are designed to carry larger loads compared to ball bearings. The drawback of this type of bearing is that it cannot handle thrust loads.
Considerations for Choosing a Bearing:
- Roller bearings are suitable for handling high radial loads. They are not ideal for high speeds due to
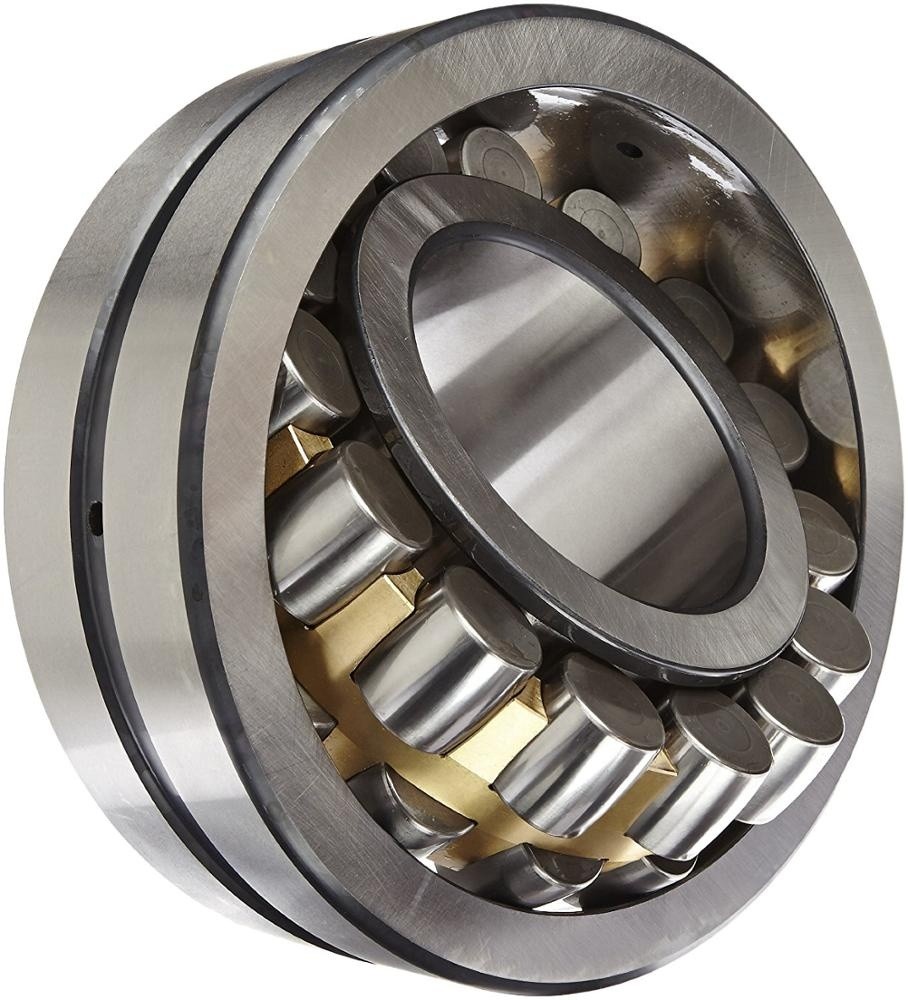

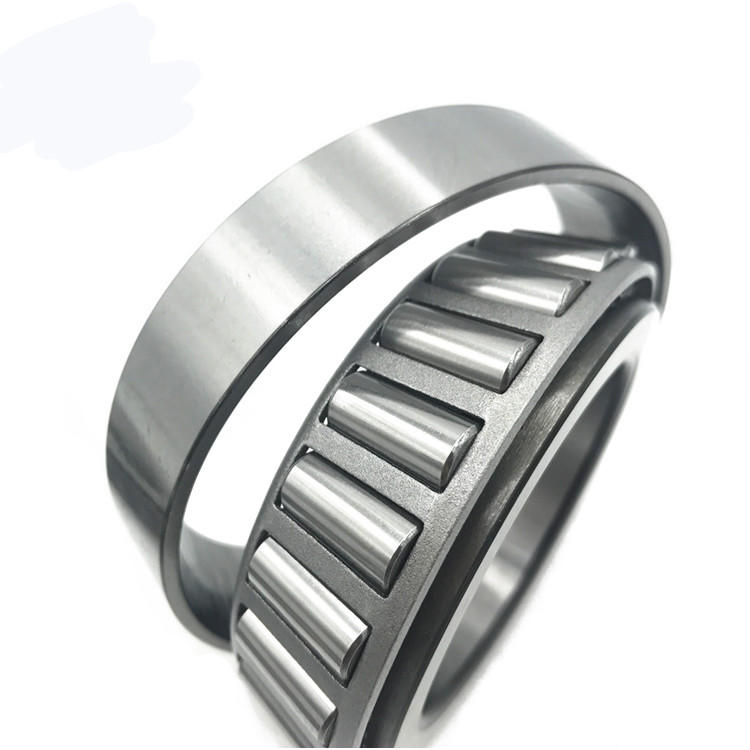
3. Tapered Roller Bearing
This bearing is commonly found in the automotive industry, especially in heavy vehicles. It has two rollers positioned opposite each other—one inside and one outside. With this structure, the bearing can withstand rotational loads from both directions simultaneously.
Considerations for Choosing a Bearing:
- This type can be applied to heavy machinery.
- This bearing is often used in the automotive industry.

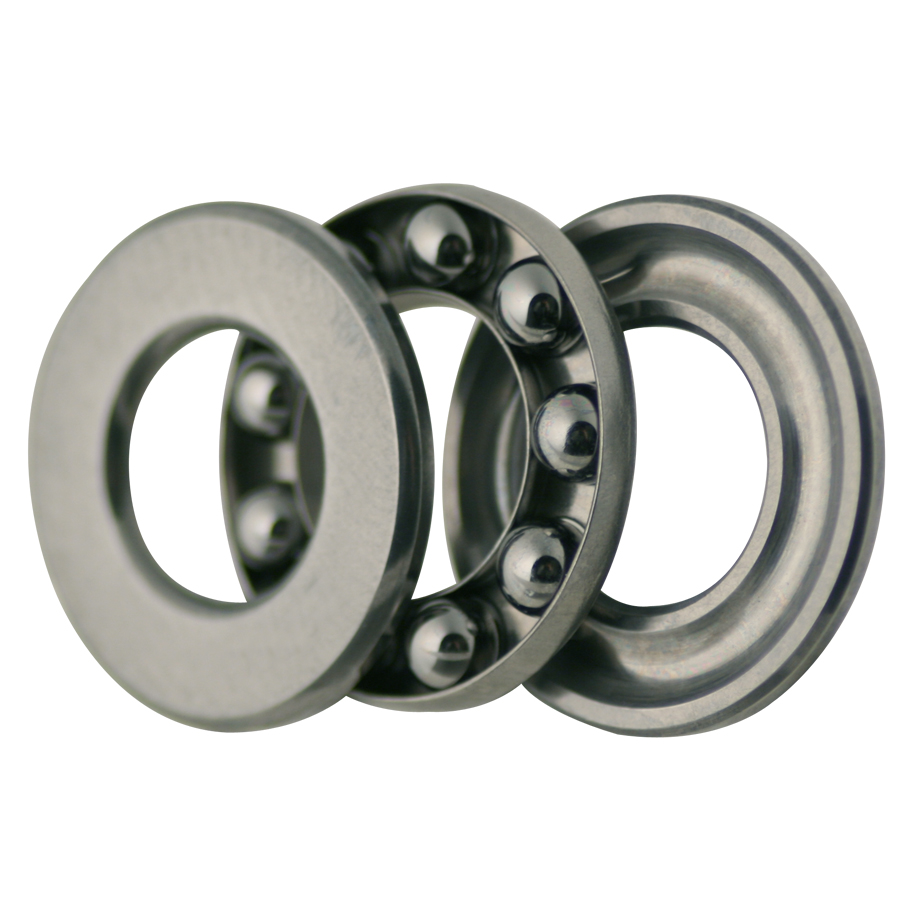
4. Ball Thrust Bearing
This type of bearing can only be used for objects with low rotational forces. Examples of its applications include swivel chairs and rotating tables. Therefore, this bearing cannot handle radial loads.
Considerations for Choosing a Bearing:
- This bearing can only be used for low rotational forces.
- It is ideal for use when the primary load is axial.

5. Magnetic Bearing
This type of bearing can be considered the most modern. It operates with an internal magnetic system. The advantage of this bearing is that it has very high-performance capabilities.
Considerations for Choosing a Bearing:
- This bearing is suitable for high-speed applications.
- It is ideal for use in lubrication-free constructions, such as in the food or pharmaceutical industries.
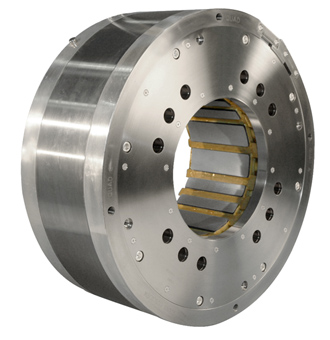
6. Roller Thrust Bearing
This bearing has a shape similar to a roller bearing, but what distinguishes it is its position in the application.
Considerations for Choosing a Bearing:
- This bearing is suitable for withstanding radial loads.
- It can be applied to rotational speeds ranging from medium to high.

Written by: Pradhita Novwantama S. (Manufacturing Design – ATMI Polytechnic Surakarta)


