The Maternal and Child Health Program (MCH) is a service program aimed at pregnant women, other mothers, postpartum mothers, family planning, and infants. This program aims to reduce maternal and infant mortality through intensive health services at puskesmas. Given that maternal and infant mortality rates in Indonesia are still high.
Since the time of pregnancy, the mother must get intensive health services to prepare for the birth of her baby. At the puskesmas, pregnant women can follow some of the MCH provided. What are the MCH programs that pregnant women can join? Check out more in the following article.
Read More: Complete! This is the MTBS Service Flow at Puskesmas in Indonesia
15 Maternal and Child Health Programs
The MCH program is one of the public health efforts that focuses on maternal, infant, toddler, and family planning services. Through ANC and PNC services, childbirth with competent health workers, immunization, to early initiation of breastfeeding and exclusive breastfeeding. Here are 15 maternal and child health programs that can be followed at local health centers based on MCH Book guidelines from the Ministry of Health:
1. Pregnant Women Class
The pregnant women class is an MCH program that aims to provide information about pregnancy, childbirth, postpartum care, newborn care, nutritional needs and fulfillment, and health services that must be received. This program can be attended by pregnant women at least once and can be accompanied by their husbands. In class, pregnant women accompanied by cadres will provide complete information.
2. Monitoring Pregnant Women at Risk
The monitoring program for at-risk pregnant women is one of the MCH programs to educate at-risk pregnant women by maintaining health and nutritional intake during pregnancy. The education provided includes danger signs during pregnancy, postpartum mothers, postpartum mothers, newborns, where and where to seek help. This mentoring program is carried out intensively by providing care and actions that are quickly adjusted to the condition of pregnant women. So that mothers can give birth to babies healthily and safely accompanied by health workers.

3. Monitoring of Postpartum Mothers at Risk
Monitoring postpartum mothers at risk serves to educate mothers about pregnancy and childbirth health through supplementary feeding (PMT). The puerperium period is the recovery period of the mother’s reproductive organs after childbirth which lasts about 42 days. During this puerperium, the mother’s body experiences physical to mental changes such as discomfort in the breasts, vagina, cramps, abdominal pain, vaginal discharge, changes in skin and hair, and emotional changes.
During the postpartum period, mothers are encouraged to do an examination at the village midwife or at the puskesmas. Medical examination for postpartum mothers is divided into several stages, including:
- The first examination is at 6 hours to 3 days after delivery.
- Second examination at 4 to 28 days.
- The third examination is on 29-42 days.
The examination of postpartum mothers begins with an interview by health workers followed by a health examination of vital signs, uterus, breast, to psychic.
4. Neonatal Monitoring at Risk
Monitoring programs for neonates or newborns at risk are included in the MCH program. This program is certainly useful for monitoring the health of newborns.
This monitoring includes APGAR (appearance, pulse, grimace, activity, and respiration) assessments 2 times in the first minute and 5 minutes after birth. In addition, examination also of congenital abnormalities, namely the presence or absence of developmental abnormalities in the baby’s body. Furthermore, a physical examination is also carried out including length, height, head circumference, anus, mouth, feet, hands, to weight.
Read More: Tips for Choosing a Safe and Appropriate Patient Bed
5. Family Planning Counseling
Family planning counseling program after childbirth. This program is used for the use of contraceptives directly after childbirth for up to 42 days. The objectives of this program are as follows:
- To adjust the distance and prevent pregnancy from getting too close. It is recommended that the distance between childbirth should be 2 years.
- Preventing unwanted pregnancies
- Maintain and improve the health of mothers, babies, and toddlers.
- Mother can have enough time for herself, her child, and her family.
6. Nutrition Services (PMBA and Vit A) & Deworming
Nutrition services in the provision of PMBA (infant and child feeding), vitamin A, and deworming are also included in monitoring maternal and child health. Vitamin A is used to increase the baby’s body’s resistance to diseases and infections such as measles and diarrhea. While deworming is used for:
- Optimization of absorption of carbohydrates, proteins, vitamin A, and iron.
- Reduce stunting in children.
- Kills various types of worms.
7. SDIDTK Services
SDIDTK services which stands for stimulation, early detection, and intervention of growth and development is an activity to monitor the growth and development of toddlers aged 0-72 months or 5 years. This monitoring is carried out every 6 months at puskesmas and posyandu. This SDIDTK service activity includes weighing toddlers, measuring height, and toddler body length, to measuring the circumference of the upper arm and head as a child’s developmental status.
SDIDTK activities aim to determine growth deviations in children. This deviation, for example, malnutrition, can be prevented as early as possible so that conditions of failure to grow in the long term so that stunting can occur.
8. Immunization Services
Often when mothers come to puskesmas or posyandu there are immunization services. Moreover, there is a simultaneous national immunization month, where toddlers get immunization at posyandu. It turns out that this immunization service is an effort to increase children’s immunity to a disease so that children are not susceptible to disease in their infancy. Immunization is carried out from 0-12 months of age. This immunization includes HB vaccines for measles.
Read More: The Best Recommendation of Gynecological Examination Table in 2024
9. Adolescent Reproductive Health
Reproductive health services can also be an MCH program at puskesmas. Reproductive health is a health condition physically, mentally, and socially, free from disease in the function and production process. This service aims to prevent and protect adolescents from sexual behavior that can affect reproductive health. In addition, it is also to prepare adolescents to lead a healthy reproductive life and prepare to become mature parents. This production health program is carried out by educating adolescents through youth posyandu.
10. Toddler Mother Class
The next program is a class for mothers of toddlers. This program aims to provide information related to parenting according to the age of children. So that parents can be educated and can monitor children’s development in a structured manner. In addition, this program can provide important information on children’s growth and development, such as nutrition, immunization, toddler care, to the treatment of children when sick.
The assistance of this class for mothers of toddlers is carried out by posyandu cadres and puskesmas officers. Here mothers can discuss, exchange opinions, and exchange experiences between parents in parenting.
11. Fulfillment of Nutrition and Child Care After Birth
After the child is 6 months old, complementary foods must be given, namely complementary foods. In providing complementary foods, mothers must know what foods can and cannot be given to children. For this reason, mothers need to take this nutrition fulfillment class at the puskesmas. This program is carried out like a class on making complementary foods from carrots, meat, vegetables, tempeh, and others.
It is hoped that through this program mothers can be educated and can apply complementary food to children. In addition, the provision of good complementary food must certainly be timely, adequate, safe, and given correctly.
In addition to fulfilling nutrition, it is also accompanied by education on child care after birth. Treatment in this child is done by treating the body, teeth, the mouth. Also, get used to children to wash their hands and cut their nails.
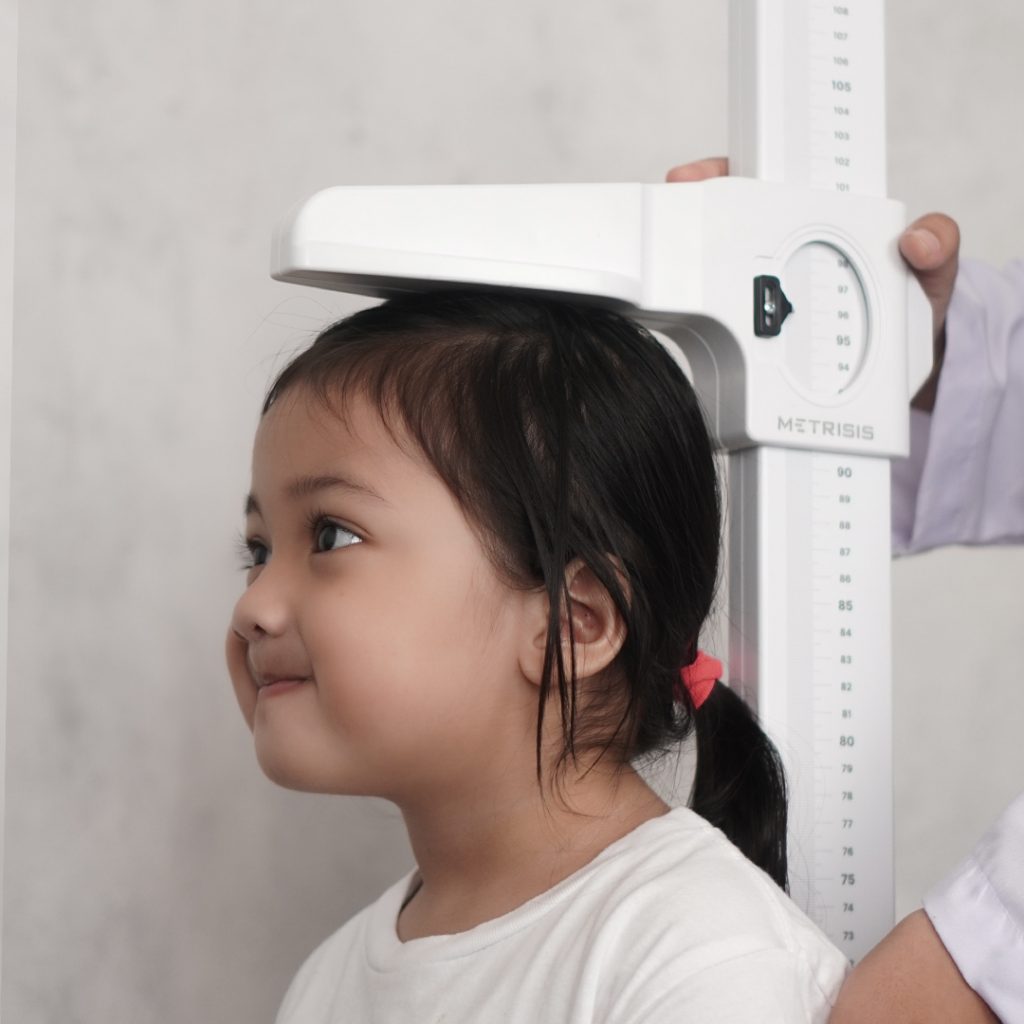
12. Physical examination of child anthropometry
Things that should not be missed in the growth and development of children are monitoring their growth through anthropometric physical examination. This aims to find out the nutritional status of children. An anthropometric examination can be through measuring height and body length, weight, and the circumference of the upper arm and head.
Through anthropometric examination, it can be known the growth graph according to its age, the results of which are recorded through the MCH book. It can also identify whether children are stunted or not. So it is very important to do anthropometric examinations from the age of 0-5 years.

13. Environmental Health and Safety
To create a safe and comfortable family, parents can monitor the environmental safety of children. Avoid children from hazardous materials such as fire, and electricity that can be dangerous.
In addition, protects children from physical, psychological, and sexual violence, and neglect. Keep children away from violence such as:
- Pinching and hitting
- Mocking and threatening
- Sexual violence
- Neglect, non-fulfillment of nutrition, health, and education.
To avoid this, parents can build communication with children. For example, inviting children to tell stories, listening to children’s complaints, and respecting children’s opinions.
14. Child Friendly Service
Child-friendly services are services that aim to fulfill, protect, and respect children’s rights by child protection principles. With this, it is hoped that children’s health can be fulfilled so that problems in children can decrease.
15. Care of a Sick Child
The next program is the treatment of sick children. Maybe some parents are still confused about caring for children when sick. At the puskesmas, mothers can take classes to care for sick children so that mothers can be educated. For example, if the child is sick with a fever, the mother can do a compress with warm water or give febrifuge. But if the fever does not go down, the mother must take the child to a health care facility to get intensive care.
Read More: What’s The Difference Between Physical and Diagnostic Examination?
MCH Service Support Facilities at Puskesmas
In maximizing maternal and child health services in Puskesmas, health equipment is needed that supports MCH sets. Among these are equipment:
- Checkable
- Check bed
- Action table
- Sphygmomanometer
- Gynecological table
- Fetal doppler
- Infusion pole
- Check light
- Wheelchair
- Baby basket or baby box

If you are looking for MCH service support equipment at the puskesmas, we PT Solo Abadi Indonesia provide your various needs. You can easily get this equipment through us by contacting our Admin via WhatsApp. In addition, it is also available in our E-Catalog here. Don’t forget to get the latest information from us at www.soloabadi.com.


